Learning
0 Discovered URLs in GSC? Fix 100% Tips
Highlight:
- Understanding the Issue: “0 Discovered URLs” in GSC indicates that Google is aware of your pages but hasn’t indexed them. It’s crucial to address this for optimal site visibility.
- Common Causes: Issues can range from technical glitches, incorrect robots.txt settings, crawl budget limitations, and poor site structure.
- 100% Fixed Tip: Instead of submitting a primary sitemap, directly submit sub sitemaps like: page_sitemap.xml, product_sitemap.xml, etc., for a more effective indexing process.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regular checks on GSC, swift error resolutions, and staying updated with SEO best practices ensure sustained site health.
1. Introduction
One day, Google Search Console showed “0 Discovered URLs” for my website. Why? What went wrong? I dug deep, found out why, and fixed it. I’ll share what I learned in this guide and how you can fix it. Let’s get started.
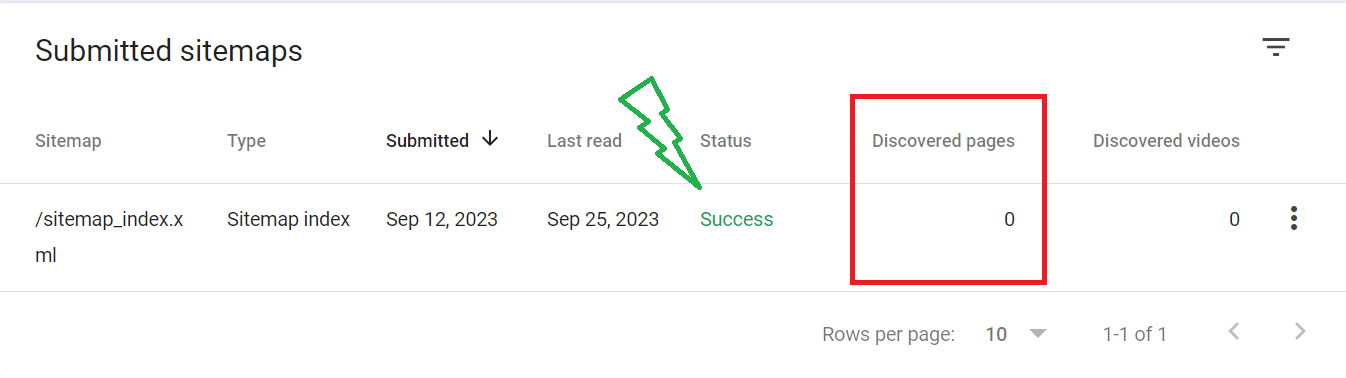
2. Understanding the Basics
Suddenly, seeing “0 Discovered URLs” can be confusing. Before diving into fixes, let’s understand what this means and why it matters.
2.1. What does “0 Discovered URLs” mean?
When Google’s bots roam the web, they find (or “discover”) pages. These discovered pages are then indexed, meaning they can appear in search results. If GSC shows “0 Discovered URLs,” it means Google knows about your pages but hasn’t added them to its search results yet.
2.2. Why is it crucial to address this Issue?
Your website’s visibility is at stake. If your pages are indexed, people can find them on Google. If you’re running a business, this can hurt your website’s traffic and potential sales.
2.3. Is “0 Discovered URLs” Affecting Website Ranking?
You may worry when “0 Discovered URLs” appear in your Google Search Console. But the big question is: How does this impact my website’s ranking? Let’s explore the potential repercussions of this Issue on SEO and site rankings.
2.3.1. The Direct Consequences of SEO
When Google hasn’t indexed your pages, they won’t appear in search results. This directly affects:
- Visibility: Your site’s visibility takes a hit, leading to a potential drop in organic traffic.
- User Engagement: Crucial content might be hidden from users, leading to decreased engagement and potentially higher bounce rates.
- Site Authority: Persistent indexing issues might signal underlying problems to Google, affecting your site’s perceived authority and trustworthiness.
2.3.2.Real-World Impact on Rankings
Based on my research and experience:
- Short-Term Impact: There might be a temporary dip in rankings as Google re-evaluates your site’s relevance and authority. For instance, according to a discussion on Webmasters Stack Exchange, it can take about 7-10 days from submitting URLs via GSC for them to influence the number of pages Google displays.
- Long-Term Impact: If addressed promptly, there’s minimal long-term impact. In fact, by identifying and fixing underlying issues, your site might emerge stronger in search rankings. Rank Math emphasizes that Google can discover URLs without the sitemap, and the sitemaps only act as a guide. This means that even if your sitemap shows “0 Discovered URLs,” other factors might affect your site’s visibility.
While “0 Discovered URLs” can be concerning, understanding its implications and addressing it promptly can prevent any significant impact on your site’s ranking. It’s essential to stay informed, monitor your GSC regularly, and take proactive measures to ensure your site remains in good standing with search engines.
3. Common Reasons for 0 Discovered URLs
When faced with the “0 Discovered URLs” issue, it’s essential to pinpoint the root cause. Here are some common reasons and their brief explanations:
3.1. Technical glitches and server errors
Sometimes, the problem isn’t with your site but with Google itself. Technical hiccups on their end can lead to temporary indexing issues. Additionally, if your server frequently times out or faces errors, Google might need help accessing your pages.
3.2. Issues with robots.txt and meta tags
Your robots.txt file tells search engines which pages to look at and which to ignore. If set up correctly, it might allow Google to see your pages. Similarly, meta tags on your pages can prevent indexing if they contain “index” directives.
3.3. Crawl budget limitations
Google doesn’t have unlimited resources. It allocates a “crawl budget” to each site, determining how many pages it’ll check in a given time. If your site has many pages or changes often, some might need to be included.
3.4. Site structure and internal linking problems
A well-organized site with clear internal links helps Google understand and index your content. Some pages might be overlooked if your site’s structure is messy or lacks internal links.
Having identified potential causes, the next step is finding solutions. But before diving into that, it’s essential to grasp these foundational issues.
4. Proven Tips for a 100% Fix
Encountering the “0 Discovered URLs” dilemma can be a bit of a shocker. But, with a systematic approach, it’s entirely manageable. Here’s a breakdown of actionable solutions based on my hands-on experience:
Tip 1: Double-Check Your robots.txt
Your robots.txt file guides search engines, telling them which parts of your site to explore and which to skip. Mistakes here can inadvertently block Google. Make sure:
- Essential pages aren’t being blocked (like Page, Post, products…)
- Directives are clear and correct.
- Use online tools to validate your robots.txt, ensuring it’s set up correctly.
Example of Blocked by robots.txt for Post:
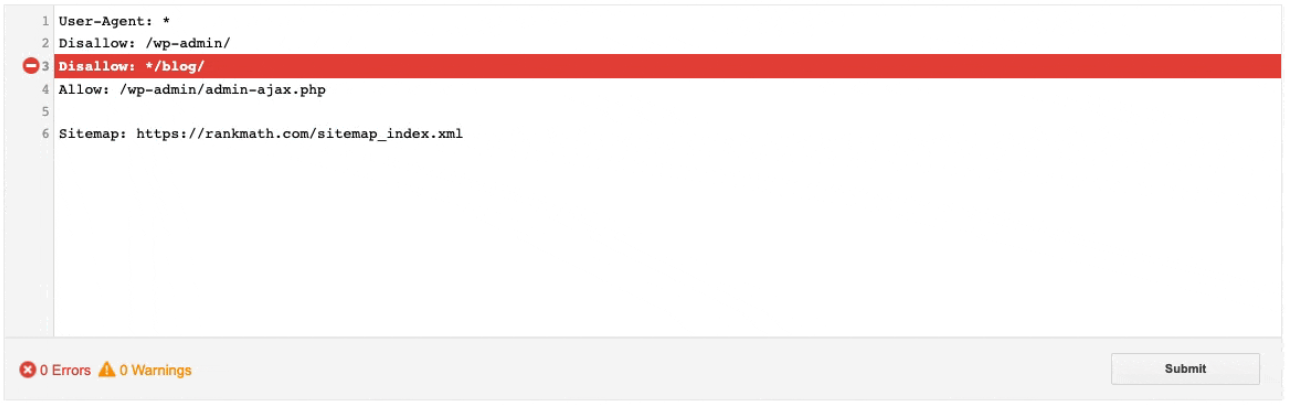
Tip 2: Prioritize Quality Content – Deliver Value and Originality
Google loves content that stands out and offers genuine value to readers. To make your site irresistible:
- Ensure content is unique and not duplicated elsewhere.
- Regularly update and refresh old content.
- Remove or revamp thin content that doesn’t add much value.
Tip 3: Address Technical Aspects
Crawl Budget and Server Health
Google allocates a specific “crawl budget” to each site. To make the most of it:
- Optimize your site’s loading speed.
- Ensure your hosting server is reliable and doesn’t frequently time out.
- Use a sitemap to guide Google to your key pages for extensive areas.
Tip 4: Enhance Internal Linking and Organization
A logically structured site helps Google and its users alike. To optimize:
- Organize content into clear categories.
- Use internal links to connect related content.
- Ensure essential pages are easily accessible.
Tip 5: Dive into the URL Inspection Tool
Google Search Console isn’t just for identifying problems; it’s also a part of the solution. With the URL Inspection Tool:
- Check the status of individual URLs.
- Identify and rectify any issues.
- Directly request Google to index specific pages.
By tackling each tip step by step, you’ll be well on your way to resolving the “0 Discovered URLs” challenge and ensuring your site shines on search results.
Tip 6: Submit Individual Sitemaps
While most websites submit a primary sitemap like domain/sitemap_index.xml to GSC, sometimes this can lead to the “0 Discovered URLs” Issue. If you’ve ensured there’s no other problem, a straightforward solution is at hand:
- Instead of relying solely on the main sitemap index, delve deeper.
- If your sitemap_index.xml includes sub-sitemaps like page_sitemap.xml, product_sitemap.xml, post_sitemap.xml, and local_sitemap.xml, submit them individually.
- By directly submitting these individual sitemaps, you’re giving Google a more precise roadmap to your content.
- This method has proven to be a 100% successful fix in many cases, ensuring that Google can effectively read and index your content. And here’s the proof…
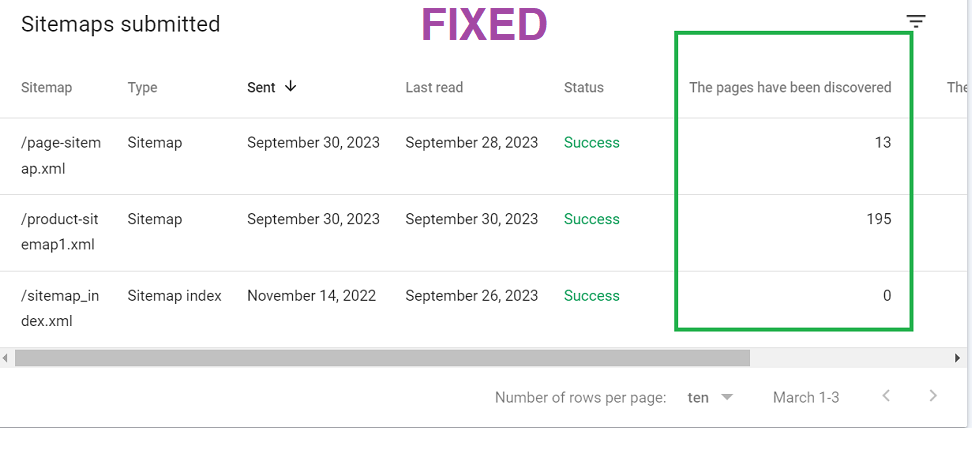
5. Monitoring and Maintaining URL Health
Ensuring your URLs are discovered and indexed is just the beginning. Continuous monitoring and proactive maintenance are essential to sustained SEO health. Here’s how to stay on top of it:
5.1. Stay Updated with Indexing Status
Google Search Console is your primary tool to understand how Google views your site. Make it a habit to:
- Check GSC regularly for any crawl or indexing issues.
- Address errors or warnings promptly to prevent them from escalating.
5.2. Keep Your Site Bug-Free
Technical issues can pop up unexpectedly. To ensure they don’t hinder your site’s indexing:
- Monitor server uptime and address any frequent downtimes.
- Regularly audit your site for broken links, server errors, or other technical glitches.
5.3. Keep Learning and Adapting
The world of SEO is ever-evolving. To ensure your site remains in good standing:
- Stay updated with Google’s guidelines and algorithm updates.
- Join SEO forums, attend webinars, and read trusted SEO blogs to keep your knowledge fresh.
These practices will address the “0 Discovered URLs” issue and fortify your site against future SEO challenges.
6. Further Learning Resources on “0 Discovered URLs in GSC”:
For those keen on diving deeper into the topic, here are some external resources that provide valuable insights:
(a) Sitemap is submitted into GSC but shows 0 Discovered URLs – A discussion on Google’s official support forum addressing the Issue.
(b) Google indexed my sitemap successfully but showed 0 URLs discovered – A thread on Webmasters Stack Exchange where users share their experiences and solutions.
(c) 0 discovered URLs in sitemap in Google Search Console – A detailed post on WordPress’s official forum where users discuss the Issue and provide potential fixes.
(d) Why are there 0 discovered URLs after submitting my sitemap in GSC – A Reddit thread where users share their experiences and seek solutions?
These resources offer a mix of expert advice, community experiences, and practical solutions to help address the “0 Discovered URLs” Issue in GSC.
7. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1: What are discovered URLs?
Q2: Why is discovered currently not indexed?
– Crawl Budget: Google allocates a certain number of pages to crawl on a site within a given timeframe. If the budget is exhausted, some pages might be left out.
– Technical Issues: Problems like server errors, noindex directives, or blocked resources can prevent indexing.
– Low-Quality Content: If Google deems the content as low quality or duplicate, it might choose not to index it.
– Site Structure: Deeply nested or unlinked pages need to be noticed.
Q3: Why is my URL not indexed?
– Robots.txt: Ensure that the URL isn’t blocked in the robots.txt file.
– Meta Tags: A “no index” meta tag will prevent the page from being indexed.
– Canonical Issues: Ensure there is only one version of the URL; it needs to be more prominent.
– Google Penalties: Violations of Google’s guidelines can lead to de-indexing.
Q4: What are the 3 URLs?
Absolute URLs: These specify the full path, like “https://coursehuge.com/shop.html“.
Relative URLs specify only a partial way, like “/page1.html”.
Root-relative URLs start from the root directory, like “/images/pic.jpg.”
Q5: How does URL search work?
– Search engines use bots to navigate the web and find new content.
– Processing: The content is analyzed for relevance and quality.
– Indexing: The page is added to the search engine’s database, making it searchable by users.

